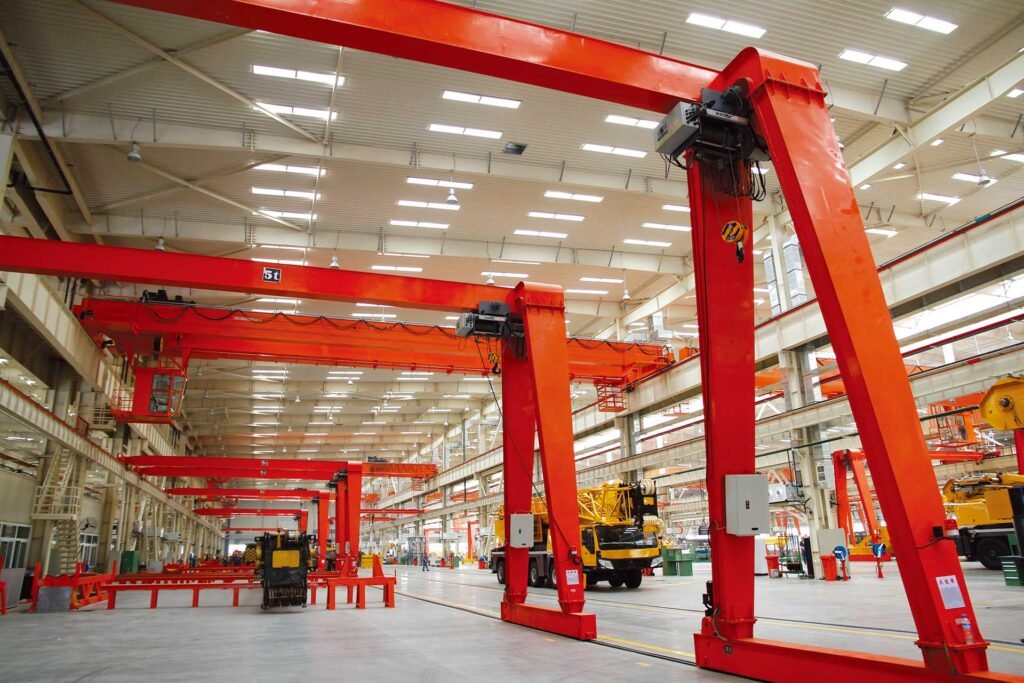
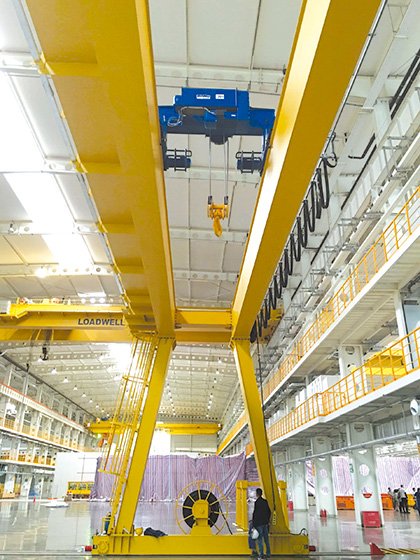
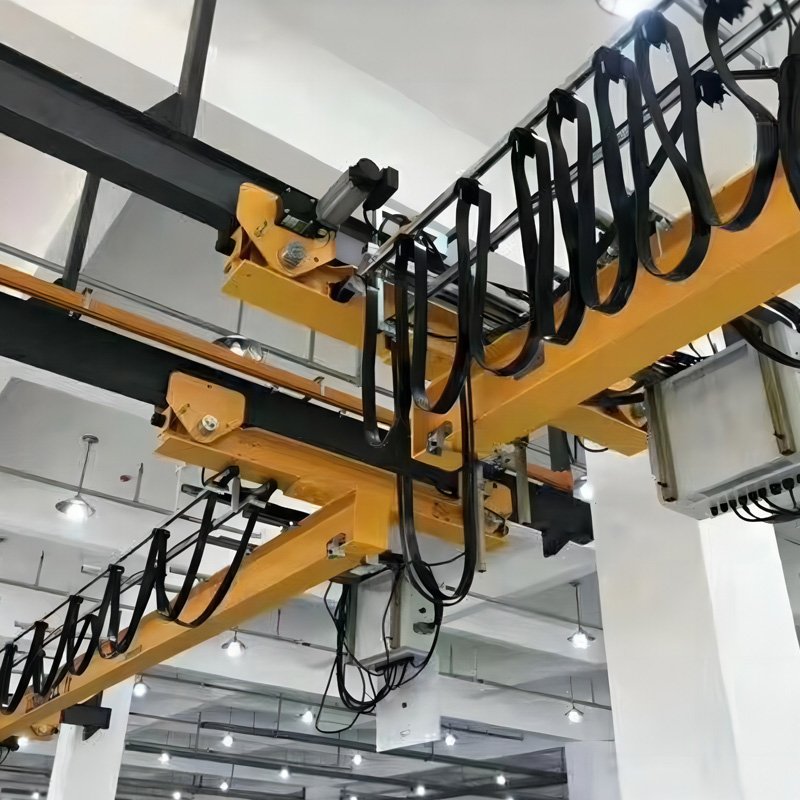
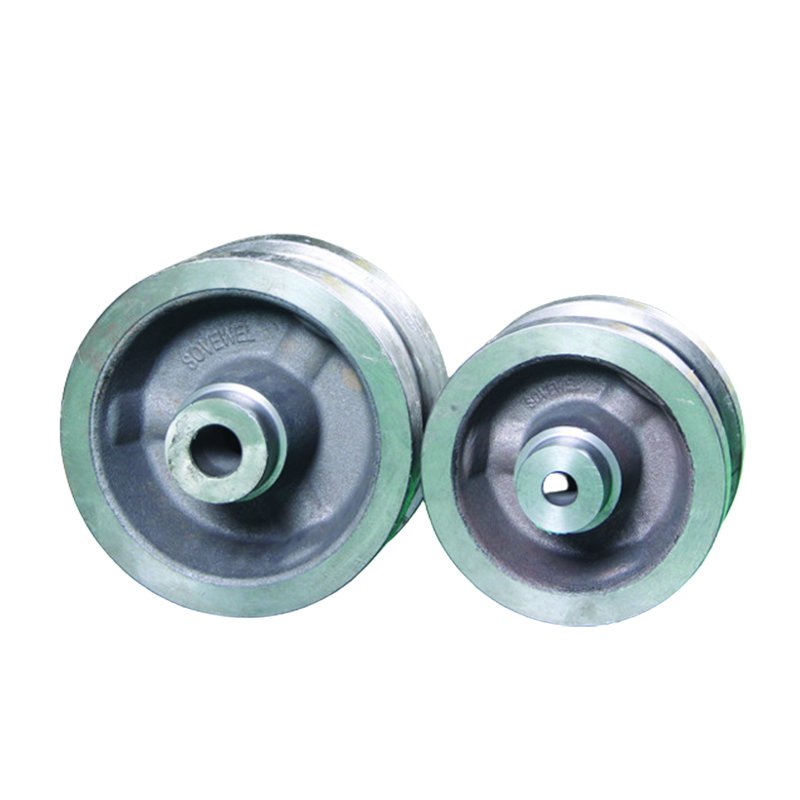
In industrial lifting equipment, gantry crane parts are not isolated components assembled at random. They form a coordinated engineering system based on structural mechanics, drive technology, electrical control, and safety design.
The overall performance of a gantry crane is largely determined by three core factors:
- Whether critical crane components are properly selected
- Whether different systems are correctly matched and integrated
- Whether key elements can maintain stable performance under long-term operating conditions
For plant managers, engineers, and equipment buyers, understanding how major crane components work together is essential for safe operation, reduced maintenance costs, and extended service life.
This guide provides a structured explanation of the functions, configuration logic, and engineering principles behind modern gantry crane systems.

1. System Structure of a Gantry Crane
Engineering-Based System Classification
From an engineering perspective, a complete gantry crane can be divided into five interrelated systems:
| System | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Structural system | Supports and transfers all working loads |
| Hoisting system | Provides vertical lifting and positioning |
| Travel system | Enables horizontal movement |
| Drive and control system | Regulates speed, direction, and precision |
| Safety system | Prevents overload, misuse, and accidents |
Each system consists of multiple gantry crane parts that work together through defined load paths and control logic.
Load Transfer Path and Critical Stress Points
During operation, loads are transferred through a clearly defined mechanical path:
Hook → Wire Rope or Chain → Drum → Hoist → Main Girder → Legs → Wheels → Rails or Ground
Any weakness in a load-bearing component along this path can reduce the overall safety margin. For this reason, critical crane elements must be evaluated as part of an integrated system rather than as standalone items.
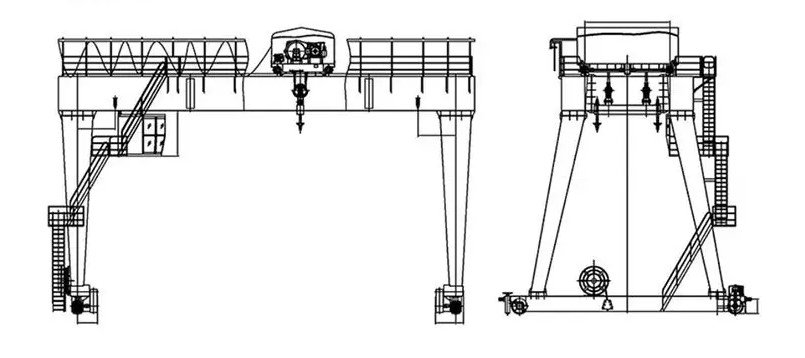
2. Hoisting System Components
The hoisting system is the core functional unit of a gantry crane and directly determines lifting capacity and operational efficiency.
Hoist and Its Engineering Role
The hoist is the primary lifting component responsible for vertical motion. Its configuration is closely related to:
- Rated lifting capacity
- Lifting height
- Duty class
- Lifting speed
A well-designed hoist supports smooth operation during frequent start and stop cycles while minimizing mechanical shock and fatigue stress.
Wire Rope, Drum, and Lifting Devices
Several key components work together to carry and transfer the load:
- Wire rope or chain
- Drum
- Hook or lifting device
Material strength, surface treatment, and structural design directly influence safety margins and service life, particularly in heavy-duty or high-frequency applications.
3. Structural and Supporting Components
Main Girders and End Trucks
The structural system forms the backbone of a gantry crane.
Key load-bearing elements include:
- Main girder
- End trucks
- Legs and portal frame
These structures are typically fabricated from welded steel and engineered based on span, load, and duty class calculations to ensure sufficient rigidity under maximum working conditions.
Structural Stability and Stiffness Control
Structural design focuses on controlling:
- Deflection
- Torsional deformation
- Dynamic load effects
Proper stiffness management is essential for long-term stability and reliable operation.

4. Travel System and Operating Accuracy
The travel system allows the gantry crane to move loads horizontally within the working area.
Core motion-related components include:
- Wheels
- Bearings
- Rails
Design priorities include smooth movement, accurate positioning, and resistance to wear and fatigue, all of which directly affect operational reliability.
5. Drive and Control Systems
Motors, Gear Reducers, and VFD Technology
The drive system typically includes:
- Electric motors
- Gear reducers
- Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) systems
VFD technology enables smooth acceleration and deceleration, precise speed control, and improved energy efficiency while reducing mechanical stress.
Braking and Limit Control Devices
Safety-critical control devices include:
- Disc brakes
- Lifting limit switches
- Overload protection devices
These systems respond quickly to abnormal conditions and help prevent accidents during crane operation.
6. Electrical and Operating Systems
Electrical Control Systems
These systems are generally composed of:
- Control cabinets
- Electrical components
- Wiring systems
In industrial environments, these systems must provide reliable protection against dust, moisture, and electrical interference.
Operating Devices and Ergonomics
Common operating methods include:
- Pendant control
- Remote control
- Cabin control
Each option offers different advantages in terms of safety, control accuracy, and operator comfort.
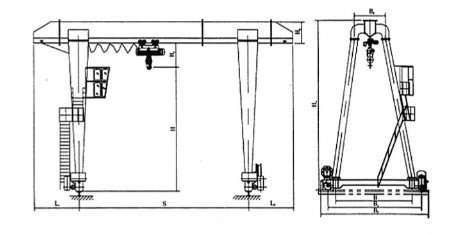
7. Safety Systems and Protective Devices
Safety systems are a fundamental requirement in modern gantry crane design.
Key protective devices include:
- Emergency stop systems
- Limit switches
- Overload protection systems
A layered safety approach significantly reduces operational risks and supports compliance with applicable standards.
8. Component Configuration for Different Applications
Indoor Industrial Applications
Typical priorities include:
- Operating frequency
- Positioning accuracy
- Efficient use of available space
Outdoor and Heavy-Duty Applications
Additional considerations include:
- Corrosion protection
- Environmental resistance
- Higher structural safety factors
These conditions place greater demands on materials, coatings, and long-term durability.
9. Selection, Maintenance, and Lifecycle Management
Selecting suitable crane components requires a comprehensive evaluation of:
- Load capacity and span
- Operating duty and frequency
- Environmental conditions
Regular inspection and preventive maintenance help extend service life, reduce unplanned downtime, and control long-term operating costs.

Conclusion
A systematic understanding of gantry crane parts is essential for achieving safe, efficient, and sustainable crane operation. From design and manufacturing to installation and maintenance, an engineering-oriented approach ensures long-term performance and reliability.
Manufacturers with strong engineering capabilities, such as Yonghao Crane, typically focus on system-level optimization rather than simple component assembly. This approach forms the foundation of dependable lifting solutions across a wide range of industrial applications. Email: yonghaoqizhong@163.com





